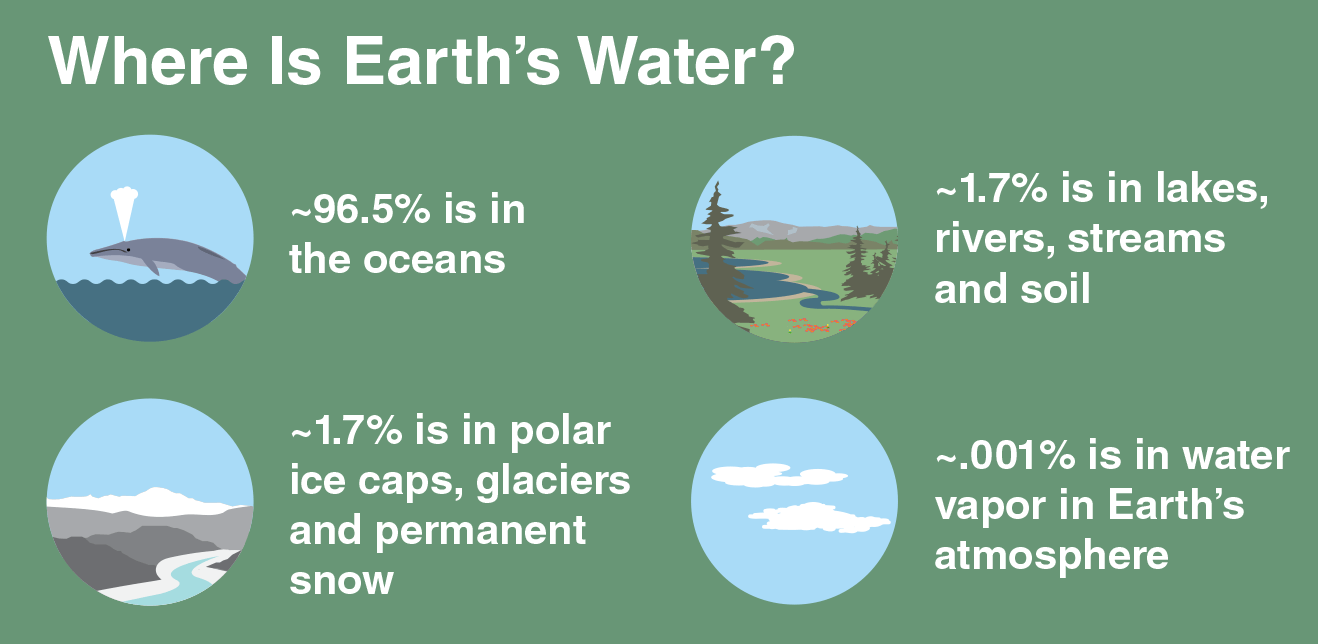
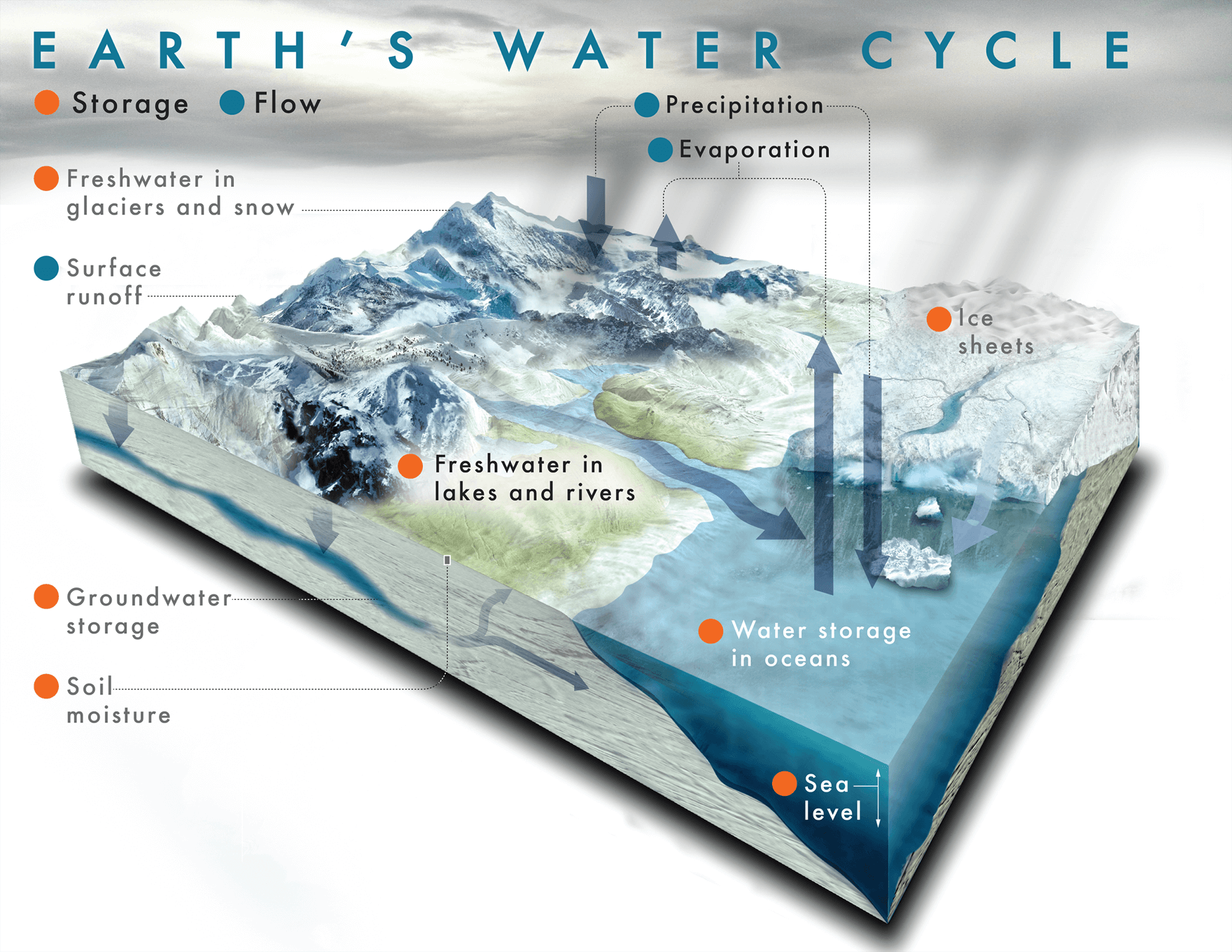
Aim: To look at the causes of climate change and how to prevent it.
As you watch the video answer these questions:
What is our greatest threat in thousands of years?
too much pollution and the water level will rise. So climate change
How do we see climate change affecting the globe?
- I see climate change affecting the globe with the temperature witch melts the ice causing human extinction
- Cars affect our earth by letting out carbon monoxide
- With climate change I believe the there will be a lot of pollution in our world
- Also with the temperature getting warmer our world might dry up and we could die
What is needed to change history?
There is no way to change the past bet there is always a chance to change the present
Is climate change a man made disaster?
climate change is man made disaster cause of all the gas and fossil fuels has been caused by man kind an.
Dramatic action must be made in the next - years to change it?
actions must be mad in about 10 year and maybe then our planet and us might have a chance
Why is our climate changing?
people are not looking after the environment which makes a lot of pollution
What is causing the warming trend of the climate?
the carbon dioxide is trapping the heat from the sun like a blanket.
When the sun comes done it would bounce up but cause of the carbon dioxide it can't.
What is the main problem?
the main problem is the climate change cause the is causing the temperature heating up and the sea levels rising so if you think about it every thing links up to climate change
What are examples of these?
it is to hot for some animals to survive
Burning fossil fuels releases what gas?
when fossil fuels are Burning it releases nitrogen and carbon.
How much hotter now is our world?
0.77C warmer than the 1951-80 average
What do we call this global warming?
we call it climate change
How is this affecting creatures / animals like bats?
this temperature is killing the animals like bats they just can't take it
What percentage of species are near extinction?
99.9%
How could this effect the world ecosystems?
Each organism has its own part and reason. when we introduce factors such as too much carbon dioxide or methane. It destroys the balance of the ecosystem which in turn affects those who live in it. The results is global warming
What global change was seen and recording breaking last year?
2018 was the 4th hottest year on record. it was 1.5 Fahrenheit more on average set between 1951 and 1980.
How is climate change affecting our weather systems?
1.wind
2. waves
3. hydro
What is another effect of climate change?
extinction
What will happen if the ice melts in Antarctica and the Arctic?
There will be no more land
How does this affect people?
They get hot and grumpy and soon the might be dead
What other things affect oceans change?
pollution
What does too much heat do to the coral?
kills it
Why did some industries not want to stop burning fossil fuels?
maybe they didn't want to stop because they were greedy and they knew it was a way to get money.
sea levels rises by 20 cm
Investigation
You can decide on how you would like to do this investigation. Your presentation could be on the blog, slides, or power point.
Investigate the different Fossil Fuels listed?
- Coal
- Oil
Write a paragraph and upload an image about each of these renewable energies.
Solar

Solar is our sun that produces energy for us and gives us sunlight that goes into electricity. concentrated solar power systems use lenses and or mirrors and tracking systems to focus a large area of sunlight into a small beam.
Wind

Wind energy is a type of form of solar energy. Wind energy describes the process by which is used to generate electricity. Wind turbines convert the kinetic energy in the wind into mechanical power, and a generator can convert mechanical into electricity.
Waves

Wave power is the capture of energy of wind waves to do useful work. for example:
electricity generation, water desalination, or pumping water. A machine that exploits wave power is a wave energy converter.
Hydro